WHAT IS THE ‘CLASH
OF CIVILIZATIONS’ THEORY?
Clash of civilizations is the
hypothesis that peoples’ cultural and religious identities will play the primary role in international
relations.
“It is
my hypothesis that the fundamental source of conflict in this new world will
not be primarily ideological or primarily economic. The great divisions among
humankind and the dominating source of conflict will be cultural. Nation states
will remain the most powerful actors in world affairs, but the principal
conflicts of global politics will occur between nations and groups of different
civilizations. The clash of civilizations will dominate global politics. The
fault lines between civilizations will be the battle lines of the future.”
An excerpt from ‘The
Clash of Civilizations?’ by
Samuel Huntington, Foreign Affairs vol. 72 (Summer, 1993)
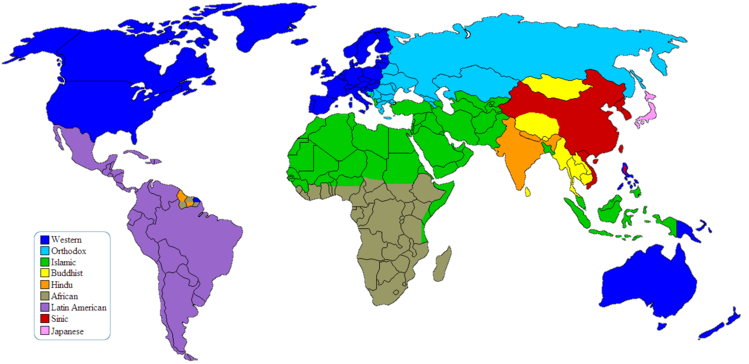
Huntington divided the world into major civilizations as we see in the map above;
Western Civilization
Orthodox Civilization
Islamic Civilization
Buddhist Civilization
Hindu Civilization
African Civilization
Sinic Civilization
Japanese Civilization
Latin American Civilization
HOW AND IN WHAT
CONTEXT IT WAS DEVELOPED
This hypothesis was first developed
at a lecture in 1992 at the American Enterprise Institute and then further
developed by Huntington in his 1993 essay on Foreign Affairs. Huntington’s thesis is viewed worldwide as the
mainstream theory explaining international relations in the post-Cold War era,
in most European and North American universities it is in the syllabus and
considered as a major work to be studied.
You can find below how often Huntington’s work appeared on top US
Universities’ reading lists:
Aforementioned, the essay was
written in 1993, so 2 years after the fall of the Soviet Union and the
argumentation goes in line with what Fukuyama and Bernard Lewis wrote those
years.
The essay was actually written in
response to his student Fukuyama’s ‘The End of History and the Last Man’ (1992).
Huntington extended his thesis with
his 1996 book ‘’The Clash of Civilizations
and the Remaking of World Order’’.
It is also remarkable that the
phrase was used in a 1990 essay called ‘The
Roots of Muslim Rage’ by
Bernard Lewis.
First of all, one should bear in
mind that all these articles/books appeared right after the collapse of the
Soviet Union, in the 1990s, when there was a vacuum in the balance of power in
the world.
There was apparently the need to
create a new antagonist; as we see in the caption in Lewis’ article; “The Roots of Muslim Rage; Why so many Muslims deeply
resent the West, and why their bitterness will not easily be mollified.” For Lewis’ article, the caption gives itself away. Lewis suggests
the inevitability of a clash between Muslims and the “West” and
implies that this hatred on the part of Muslims is unlikely to go away.
Like Lewis, Huntington warns the
reader against Islam and claims that Islamic extremism will be the biggest
threat to peace.
‘’More
recent factors contributing to a Western–Islamic
clash, Huntington wrote, are the Islamic Resurgence and demographic explosion
in Islam, coupled with the values of Western universalism—that is, the view that all
civilizations should adopt Western values—that
infuriate Islamic fundamentalists. All these historical and modern factors
combined, Huntington wrote briefly in his Foreign Affairs article and in much
more detail in his 1996 book, would lead to a bloody clash between the Islamic
and Western civilizations. The political party Hizb ut-Tahrir also reiterate
Huntington's views in their published book: The Inevitability of Clash of Civilization.
Once again, as Edward Said once
wrote, we must keep in mind the close relations between these professors and their
states’ policies, think tanks and
other institutions.
ITS ROOTS
‘Clash
of Civilizations’ was used by Albert Camus in
1946 and in 1990 by Bernard Lewis in his article ‘The
Roots of Muslim Rage’ in the
Atlantic Monthly. It derives from the phrase ‘Clash
of Cultures’ which was used in the Belle
Epoque and the colonial period. Here is an example from Louis Massignon; the
famous French Orientalist of the 20th century;
Louis Massignon, La
psychologie musulmane (1931), in Idem, Ecrits mémorables,
t. I, Paris, Robert Laffont, 2009, p. 629: "Après la venue de Bonaparte au
Caire, le clash of cultures entre l'ancienne Chrétienté et
l'Islam prit un nouvel aspect, par invasion (sans échange) de l'échelle de
valeurs occidentales dans la mentalité collective musulmane."
This thesis is part of a broader
pattern in the Orientalist literature and involves the powerful discourse that
suggests a categorical division in people’s
values and cultures. It involves the division of the world into large
geographical areas that are represented as homogenous entities,
oversimplifications, deterministic approaches and the treatment of peoples as
static objects that are primarily defined by religion or race.
See my article on Orientalism; http://kayaalpgoksu.blogspot.it/2017/06/edward-saids-orientalism.html
OSWALD SPENGLER’S ‘DECLINE
OF THE WEST’
Huntington’s book is very similar in many aspects to Oswald Spengler’s ‘Decline
of the West’ (1918, First Volume). In the
book, Spengler divides the world into 8 high cultures; Babylonian,
Egyptian, Chinese, Indian, Mesoamerican (Mayan/Aztec), Classical (Greek/Roman),
Arabian, Western or "European-American". He claims that history
should be studied through civilizations, not through ideologies or epochs, and
whole cultures evolve as organisms. Then basically he goes on to state that cultures
have a lifespan of about a thousand years of rise, and a thousand years
of decline. The final phase of each culture is, in his words, a
"civilization", very similar to what Huntington claims.
Even though Spengler’s book received a lot of criticism,
it became a really popular book in Europe in the 1920s and influenced the intellectual
atmosphere significantly.
A 1928 Time review of the second
volume of the Decline of the West described the immense influence and
controversy Spengler's ideas enjoyed in the 1920s: "When the first volume
of The Decline of the West appeared in Germany a few years ago, thousands of
copies were sold. Cultivated European discourse quickly became
Spengler-saturated. Spenglerism spurted from the pens of countless disciples.
It was imperative to read Spengler, to sympathize or revolt. It still remains
so."
Therefore,
we discover that this pattern of thinking has been a popular one since the last
century, advocating war and alarming the West about losing its ascendancy.
ARGUMENTS AGAINST IT
First of all, I don’t believe that it serves humanity to
promote such views. Claiming the inevitability of the clash between the
civilizations means advocating war and discouraging dialogue, since it suggests
that people from different civilizations cannot get on or coexist.
With its tone, it resembles the
discourse during the Cold War era, which basically said that the conflicts will
not be economic or social, they will be ideological, the ideology of the West
against the communist ideology. Again, this time, the West is the center around
which other civilizations turn, and fight against for ascendancy or dominance
it is suggested. With an aggressive tone talking about the inevitability of
clashes and aimed at opinion and policymakers, I don’t think the aim is peace and understanding.
Furthermore, it discourages the
efforts to really understand the world, people, and the human experience as a
whole since it portrays a world far from reality and disregards historical
facts. It is an oversimplification. Like Orientalism, it divides the world into
civilizations and claims that people from so-called different civilizations
have values that are categorically different from each other. It disregards the
fact that identities (whether national, religious or ‘civilizational’) are
dynamic and ever-changing, that many regions of the world have had extensive
contacts with other regions of the world, and that humans have been migrating
and going around since the dawn of history.
‘’The pyramid of civilization
isn’t the creation of a single country, a
single tribe, nor a single epoch. The story of this pyramid, which was
constructed stone by stone and stands erect thanks to the efforts of all humans
is like the story of humanity and its never-ending struggle and achievements
through history.’’
Şevket Süreyya Aydemir (1897-1976), Turkish
writer, intellectual, economist, historian
It disregards the fact that every
country, region, and city have different backgrounds. It categorizes and
classifies people and distracts us from the real sources of conflict and
problems in the world. There are countless social, economic, religious differences
within a given country or a region. Let’s take
Islam as an example. First of all, not all Muslim majority countries speak the
same language and there are multiple languages spoken in any given Muslim
majority country, as well as there are multiple religions (ancient Christian
communities in the Middle East), sects of different religions (sects within
Islam, different Christian groups such as Copts, Maronites, Melkites and other
religious groups such as the Druze and Yazidis), or groups with different attitudes towards
religion (secularist movements for instance). These are some facts to consider
before viewing a vast geographical area as a homogenous entity that acts as a
single organism. Thus, one cannot simply say the Islam in Indonesia and Morocco
are the same since there are huge differences even within countries and
regions.
I don’t think
anyone has the right to confiscate the achievements of humanity under any
exclusive banner whatsoever. I am against any kind of essentialism, in the
sense that I do not believe that there are essential, categorically different
characteristics that make one German, Italian, Western or Chinese. I recognize
the need for identity which is a human need, however, I strongly believe that
instead of promoting antagonisms and worldviews that resemble computer games
like Age of Empires, we should advocate a more profound understanding of human
experience. There is one civilization, the civilization of humanity, like Günhan Karakullukçu once said.
In addition, Western civilization
as such is an invention, or in Peter Katzenstein’s
words, it is not given but politically made. The author of ‘Civilizing the Enemy: German
Reconstruction and the Invention of the West’
Patrick Thaddeus Jackson traces the current notion of "Western
Civilization" to 19th Century German intellectuals, shows how ideas about
"The West" were transmitted to American elites via Columbia
University's "Contemporary Civilization" program.
QUOTES
‘’ Huntington is an
ideologist, someone who wants to make "civilizations" and
"identities" into what they are not: shut-down, sealed-off entities
that have been purged of the myriad currents and countercurrents that animate
human history, and that over centuries have made it possible for that history
not only to contain wars of religion and imperial conquest but also to be one
of exchange, cross-fertilization and sharing. This far less visible history is
ignored in the rush to highlight the ludicrously compressed and constricted
warfare that "the clash of civilizations" argues is the reality.’’
Edward Said (1935-2003) , professor of literature at
Columbia University, a public intellectual, and a founder of the academic field
of postcolonial studies , author of ‘Orientalism’
‘’Western civilization is not given but politically made. In this theoretically sophisticated and politically nuanced book Patrick Jackson argues that Germany's reintegration into a Western community of nations was greatly facilitated by civilizational discourse. It established a compelling political logic that guided the victorious Allies in their occupation policy. This book is very topical as it engages critically very different, and less successful, contemporary theoretical constructions and political deployments of civilizational discourse."
Peter Katzenstein, Walter S. Carpenter, Jr. Professor of
International Studies at Cornell University
‘’The pyramid of civilization isn’t the creation of a single country , a single tribe, nor a single epoch. The story of this pyramid, which was constructed stone by stone and stands erect thanks to the efforts of all humans is like the story of humanity and its never-ending struggle and achievements through history.’’
Şevket Süreyya Aydemir (1897-1976) , Turkish
writer, intellectual, economist, historian
‘’There is only one civilization, the civilization of humanity.’’
Günhan
Karakullukçu , Turkish economist
‘’The only race I know is the human one.’’
Albert Einstein , German-born theoretical physicist
‘’It is easy to show that there isn’t a clash of civilizations. The only civilization is the civilization of humanity, constititued of different cultures and traditions and different times since not all march with the same pace and walk the same paths, but certainly what is common to human experience is much more comprehensive and profound than what divides it.’’
Renato La Valle /
Le Cronache Ottomane , Italian writer
''Some people in less-developed countries feel uncomfortable
that they are just slavishly copying other, more advanced countries; but, they
have to recognize that is what everybody has been doing all along. We copy the
good ideas and in the process we adjust them and make them a little bit better.
New ideas can come from anywhere. The basic thing, though, is that every
country has to take the insights that have been developed around the world.''
Robert Shiller , American Nobel Laureate, economist, academic
‘’Nevertheless, it cannot be said that the pre-Christian Western culture was antagonistic to the cultures of the East, for there was nothing either in the philosophy or in the secular body of Roman public law that barred adjustments and accords with peoples used to different value systems.’’
Adda B. Bozeman (1909-1994) , writer and scholar of international
relations at Sarah Lawrence College
‘’ Nancy Bisaha now offers an in-depth look at the body of Renaissance humanist works that focus not on classical or contemporary Italian subjects but on the Ottoman Empire, Islam, and the Crusades. Throughout, Bisaha probes these texts to reveal the significant role Renaissance writers played in shaping Western views of self and other.Medieval concepts of Islam were generally informed and constrained by religious attitudes and rhetoric in which Muslims were depicted as enemies of the faith. While humanist thinkers of the Renaissance did not move entirely beyond this stance, Creating East and West argues that their understanding was considerably more complex, in that it addressed secular and cultural issues, marking a watershed between the medieval and modern. Taking a close look at a number of texts, Bisaha expands current notions of Renaissance humanism and of the history of cross-cultural perceptions. Engaging both traditional methods of intellectual history and more recent methods of cross-cultural studies, she demonstrates that modern attitudes of Western societies toward other cultures emerged not during the later period of expansion and domination but rather as a defensive intellectual reaction to a sophisticated and threatening power to the East.’’
Review on Nancy Bisaha’s book ‘Creating East and West’
‘’ diversity is a feature of most cultures in the world. Western civilization is no exception. The practice of democracy that has won out in the modern West is largely a result of a consensus that has emerged since the Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution, and particularly in the last century or so. To read in this a historical commitment of the West—over the millennia—to democracy, and then to contrast it with non-Western traditions (treating each as monolithic) would be a great mistake.’’
Amartya Sen, Indian economist and philosopher
FURTHER READING AND
RESEARCH:
Oswald Spengler, Decline of the West
Huntington’s Essay
Why the Clash of Civilizations is wrong. Peter Katzenstein
Edward Said Lecture / The Myth of the Clash of Civilzations
Noam Chomsky on The "Clash of Civilizations"
Bernard Lewis’
article; The Roots of Muslim Rage
Edward Said’s
article ; The Clash of Ignorance
Nancy Bisaha’s book;
Creation of East and West
The author was born in İzmir,Turkey in 1996 and is now living in Milan, Italy. He is currently studying International Economics and Management at Bocconi University. His fields of interests are history, politics and languages , and he is generally interested in social sciences. He speaks Turkish, English, Italian and a little bit of German and Russian. He started this blog in order to share his thoughts with people, to reach people who share similar interests and to create a platform for discussion. You can reach him via e-mail.
E-mail: goksukayaalp96@gmail.com
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/goksu.kayaalp
Twitter: https://twitter.com/goksukylp
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/goksuk6/